
It is no longer news that the inflationary rate in Africa’s biggest economy has continued to defy all economic solutions owing to the latest release in July by the National Bureau of Statistics- 19.64%, the highest since September of 2005.Since the turn of the new year, the country’s inflationary trend has been experiencing an upward trajectory, accompanied with its attendant effect.
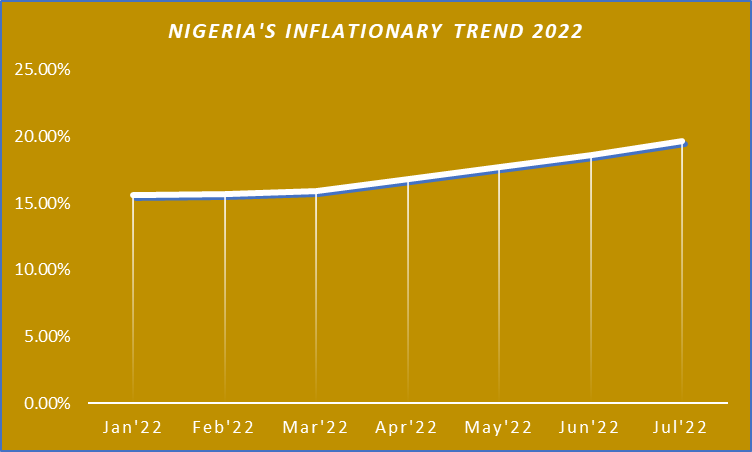
In contrast to developed nations like the USA and Japan where some level of inflation is tolerable to stimulate economic activities, Nigeria’s inflationary trend is detrimental to its growth due to its structural deficiency, logistics problems and insecurity, among others. Indeed, many of the factors that have fueled Nigeria’s high inflation are not showing any signs of receding. The most recent being higher energy prices, especially diesel, as a result of rise in oil prices.
How Inflation affects You
When prices of commodities that people ordinarily consume increase, the cost of living goes up. Their income remaining the same, they are able to buy less than before. Thus, their real income declines, and living becomes difficult.
Causes of Inflation– two schools of thought
There are two popular theories on what is responsible for inflation.
Demand-pull Inflation
Economist see this type of inflation as one caused by too much spending especially when production is weak in the economy. This is why people say inflation is too much money chasing few goods. One of the major factors driving demand-pull inflation is money supply, which is basically cash and other short-term assets that can quickly be converted to cash.
Cost-push inflation
This theory view inflation to be driven by high cost of production (wages, raw materials etc) which is then passed on to consumers. Cost-push inflation means prices have been “pushed up” by increases in the costs of any of the four factors of production—labor, capital, land, or entrepreneurship—when companies are already running at full production capacity. Companies cannot maintain profit margins by producing the same amounts of goods and services when their costs are higher and their productivity is maximized.
The price of raw materials may also cause an increase in costs. This may occur because of a scarcity of raw materials, an increase in the cost of labor to produce the raw materials, or an increase in the cost of importing raw materials. The government may also increase taxes to cover higher fuel and energy costs, forcing companies to allocate more resources to paying taxes.
What is responsible for Nigeria’s high and rising inflation rate?
According to the country’s apex bank, the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), Nigeria’s current inflation is majorly acost-push inflation one with a twist. With global energy rising amidst Russia-Ukraine conflict, the country’s main source of foreign exchange is experiencing a high fluctuation thereby impacting on the availability of forex.
In addition, the structural supply side issues such as insecurity, weather challenges, transport and distribution infrastructure still persist.
Way Forward
To address inflation, there is need to address structural issues and triggers- notably insecurity. There is need for Government to provide safe environment for any productive enterprise. It is high time investors felt safe to make investments without any form of apprehension. Also, trade policies should be aligned to encourage backward integration. No country produces all the food it consumes.
Besides, it is unlikely that the current inflationary surge will subside quickly; economic history suggests otherwise. With electioneering gaining momentum, it is time to see dirty money chasing the electorates, therefore worsening inflation.
The Center for Research in Enterprise and action in Management (CREM)can work with you to carryout any research of interest to your organization.
Please call us on 09013234481
Website: www.cremnigeria.org
Info: info@cremnigeria.org

